Alcohol and Other Drugs
Main Content

Alcohol and other drug (AOD) use plays a significant role on college campuses across the nation. Given that the misuse of substances can result in impaired judgment, altered mood and mental health, lowered cognitive ability, and legal consequences, it is important to have access to accurate information in order to make informed decisions.
ALCOHOL
Alcohol is an orally consumed substance that impacts a person’s mood, behavior, and judgment. Excessive alcohol consumption can cause brain, heart, liver, and pancreas damage. It can also lead to various cancers such as head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
Roughly 20% of college students choose not to drink alcohol. If you do decide to use alcohol, there are many strategies you can utilize to keep yourself, your friends, and others safer, including:
- Eat before and during drinking
- Have a plan to get home safely
- Pace the number of drinks per time frame
- No more than 1 drink per hour is recommended
- Alternating alcoholic drinks with water
- Don’t mix other drugs with alcohol
- Don’t leave a drink unattended
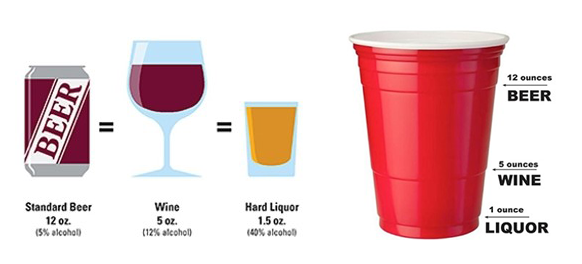
STANDARD DRINK SIZE
Not all drinks contain the same amount of alcohol, so the amount of liquid in your glass, can, or bottle does not necessarily match up to how much alcohol is actually in your drink. One unit of alcohol, or standard drink, is equal to 12oz of beer, 5oz of wine and 1.5 oz of hard liquor. Many alcoholic drinks are commonly served with more than one standard drink. Be sure to read the label to determine how many drinks you are consuming!
BLOOD ALCOHOL CONTENT
Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) is the percentage of alcohol in a person’s bloodstream due to consuming alcohol. It ranges from 0% (no alcohol) to 0.4% (potentially fatal). BAC depends on how many drinks were consumed, how quickly they were consumed, how much food was ingested prior to drinking, age, and weight. Because alcohol is a toxin to your body, if you are drinking faster than your liver can process the alcohol, intoxication occurs.
The effects of drunkenness include:
- Slurred and disorganized speech
- Poor coordination
- Disruptions in mood, behavior, and cognitive functioning
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mental amnesia
- Unresponsiveness and loss of consciousness
The impacts of intoxication increase with alcohol consumption and higher blood alcohol levels.
ALCOHOL POISONING
It is important to remember that alcohol consumption can be dangerous. Knowing the signs and symptoms of alcohol poisoning and what to do if you encounter someone who needs help can make a huge difference.
The common signs of alcohol poisoning are: unconsciousness, confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow breathing, irregular breathing, blue/pale/ashen skin and cold or clammy skin.
If you encounter someone who is suffering from any of the above conditions, it is important to help them seek medical treatment.
DO: Call 911
DON'T: Leave them alone
DO: Stay with them until medical help arrives
DON'T: Give them food, drink or medication
DO: Make sure they can breathe and are in a safe location
DON'T: Put them in a cold shower/tub
SOBERING UP
Our bodies can only metabolize, or get rid of, approximately one standard drink of alcohol per hour. Contrary to popular belief, caffeine, exercise, taking a shower or drinking water won’t help you sober up! There is no way of speeding up this process; TIME is the only solution!
CANNABIS
Cannabis is the ingestion of the chemical THC produced in the cannabis plant by smoking, vaping, eating, or dabbing. Cannabis produces an altered sense, mood changes, impaired body movements, difficulty thinking, impaired memory, hallucinations, delusions, and psychosis. Long term effects of cannabis can include lower life satisfaction, poor mental and physical health, less restful sleep, bronchitis, asthma, elevated relationship problems, and weakened academic and career success.
Cannabis affects every individual differently. The same person may have different experiences on separate occasions or across their lifespan. This can be influenced by the strength of the drug, the amount taken, and the health of the individual.
In larger amounts and concentrations, the following can occur:
- Memory impairment
- Slower reflexes
- Bloodshot eyes
- Increased heart rate
- Anxiety and paranoia
To reduce the risks associated with using cannabis:
- Purchase from a medical dispensary
- Know the CBD to THC ratio
- Vaporizers, edibles, and oils reduce the inhalation of carcinogens caused by smoking
- Avoid operating machinery after ingestion
- Waiting 3-5 hours is recommended
- Avoid synthetic products such as K2 or Spice
SIU POLICY ON CANNABIS
Marijuana is prohibited on SIU's campus. Although the state of Illinois passed a law allowing for the use of recreational marijuana, it remains illegal under federal laws. Since SIU receives federal funding, it must abide by federal laws. Anyone found with marijuana or under the influence of marijuana in any form on campus may face university, city, state and/or federal consequences. Be informed; know the laws and your Student Code of Conduct!
If you are concerned about your marijuana use and would like to talk to a professional, contact Counseling and Psychological Services at 618-453-5371 to make an appointment.
ILLICIT DRUG MISUSE
Illicit drugs are substances that are manufactured, obtained, or sold illegally. This can include illegal drugs such as heroin, cocaine, and methamphetamine, as well as the misuse of prescription drugs. Illicit drugs are highly addictive and can have serious and sometimes fatal consequences. Short and long-term health effects include cardiovascular disease, stroke, mental and cognitive disorders, organ dysfunction, and seizures. Methods of illicit drug use, particularly injection drug use, increase the risk of infections like HIV and hepatitis.
Common signs of illicit drug misuse include:
- Sudden changes in mood or behavior
- Confusion, paranoia, or hallucinations
- Slurred speech or impaired coordination
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Excessive sweating or chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of consciousness or seizures
If someone is showing these signs, especially if they are unresponsive or having trouble breathing, seek medical help immediately and administer Narcan (Naloxone) if able.
NARCAN (Naloxone)
Narcan (Naloxone) is a safe, easy-to-use medication that can reverse the effects of opioid overdose within 2–3 minutes. Narcan does not work for overdoses involving non-opioid drugs like cocaine, methamphetamine, or alcohol—but it won’t hurt if given.
Common signs of opioid overdose include:
- Unresponsiveness or unconsciousness
- Slow, shallow, or no breathing
- Blue or grayish lips and fingernails
- Gurgling or choking sounds
- Limp body
- Pale or clammy skin
- Very small (pinpoint) pupils
Narcan is available for free in the Student Health Services Vending Machine located in the Student Rec Center and the Student Health Center Pharmacy behind the counter.
Always call for emergency help, even after using Narcan, as the person may need more care.



